In the dynamic world of wireless charging, Qi wireless charging emerged as a notable standard, freeing devices from the constraints of traditional cords. It quickly became the go-to standard for powering larger devices like smartphones and tablets. However, in the ever-evolving landscape of wireless charging, NFC-Wireless Charging (NFC-WLC) has taken its own path, focusing on specific applications, and utilizing distinct power capabilities. This blog explores NFC-WLC, highlighting its unique applications, operated with short-range efficiency, compact size, fast communication, and low power consumption that differentiates it from other wireless charging standards.
What is the NFC-WLC: An overview
NFC-Wireless Charging (NFC-WLC) is an innovative wireless charging technology that caters to the specific needs of small devices, wearables, and gadgets with low power requirements. At its core, NFC-WLC operates at a frequency of 13.56 MHz and data rate up to 848 Kbit/s. What sets NFC-WLC apart is its focus on compactness and convenience.
Designed to power up small devices with a maximum output of 1W. Its small antenna sizes ranging from 3 mm to 10 mm make it an ideal choice for applications where space is at a premium.
This innovative technology combines the principles of Near Field Communication (NFC) with wireless charging. In this partnership, two key components play pivotal roles: The Wireless Charing Poller (WLC-P) is a charging transmitter, and the Wireless Charing Listener (WLC-L) is a charging receiver.
Enabling NFC wireless charging with RA12 readers
The RA12 HF RFID reader chip is a compatible option with wireless charging poller (WLC-P) device, making it a reliable choice for developing wireless chargers capable of efficient power transmission.
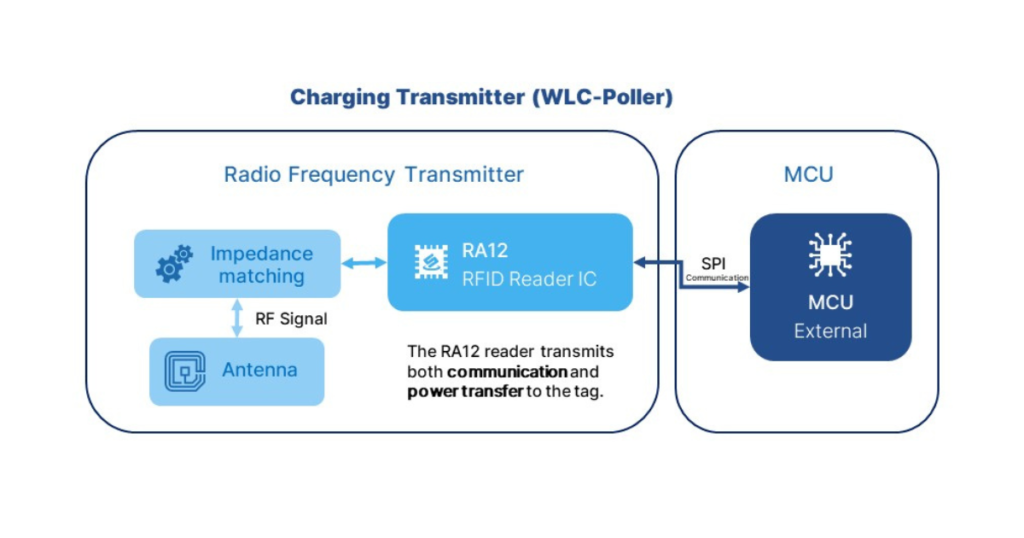
RA12: the core of the charging transmitter (WLC-Poller) block diagram.
Additional features include the RA12 chip offers efficient power-saving modes, as well as low-power card detection. It senses external cards periodically, conserving energy, and waking up the system when required. The transmitter is versatile, operating across a broad range of supply voltages to accommodate various applications such as 5V for base stations or desktop readers, and 3.3V for handheld devices. Besides, it offers a high drive current of up to 250 mA, enabling the charging of small devices.
Due to the above features, it is ideally suited to serve as the wireless charging poller (WLC-P) for your smart gadgets.

















